Discover effective coping strategies in substance abuse group therapy. Learn how group sessions foster recovery, resilience, and long-term sobriety through practical tools and shared support.
Introduction
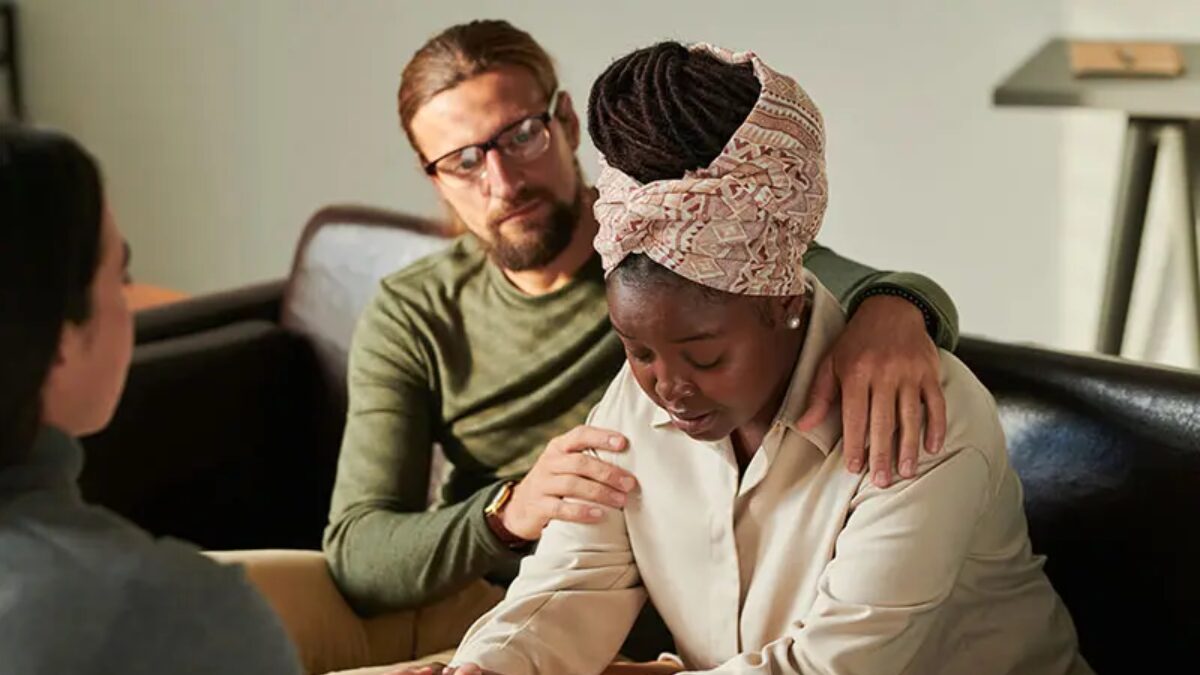
Substance abuse group therapy is a powerful tool in addiction recovery, offering individuals a sense of connection, support, and accountability. Among its key components, effective coping strategies stand out as essential for long-term sobriety and emotional stability. These strategies are not only discussed but actively practiced within a supportive environment, helping participants navigate cravings, triggers, and underlying emotional challenges.
This article delves into the most effective coping strategies in substance abuse group therapy, how they are implemented, and the role they play in recovery success. Whether you are a professional, a recovering individual, or a loved one, understanding these strategies is crucial for fostering healing and growth.
What is Substance Abuse Group Therapy?
Group therapy for substance abuse involves structured sessions led by a licensed therapist where multiple individuals come together to share experiences, challenges, and solutions. These sessions often follow evidence-based models such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), 12-Step Facilitation, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT).
The collaborative format allows participants to learn from others’ journeys, receive encouragement, and develop practical coping tools to manage their addiction.
Why Are Coping Strategies So Important?
Coping strategies are the skills and actions individuals use to manage stress, triggers, and emotional upheaval. In substance abuse recovery, these tools are crucial to avoid relapse, manage cravings, and improve overall mental health.
In a group therapy setting, these strategies are reinforced through peer feedback, shared experiences, and therapist guidance. Participants not only learn how to cope but also witness others applying these methods successfully in real life.
Common Challenges in Substance Abuse Recovery
Understanding the obstacles people face in recovery can highlight the importance of coping mechanisms. Here are some of the most frequent challenges:
| Challenge | Impact on Recovery |
|---|---|
| Cravings and withdrawal symptoms | Lead to relapse if not managed properly |
| Emotional instability | May cause impulsive behavior and substance use |
| Relationship issues | Increase stress and feelings of isolation |
| Environmental triggers | Heighten the urge to use substances |
| Lack of self-worth | Undermines motivation for sustained sobriety |
These challenges demand structured coping strategies to maintain progress and mental resilience.
Most Effective Coping Strategies in Substance Abuse Group Therapy
Below are the most impactful and widely used coping strategies taught and reinforced in substance abuse group therapy sessions:
1. Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring, a technique rooted in CBT, helps individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts. In group settings, participants work together to reframe beliefs like “I’m a failure” into “I’m working through a tough period, and I can recover.” This shared dialogue reinforces hope and accountability.
2. Mindfulness and Meditation
Group therapy often includes guided mindfulness sessions that teach participants how to stay present and manage cravings without judgment. Meditation exercises can reduce stress and improve emotional regulation, leading to better decision-making in challenging situations.
3. Role-Playing and Scenario Practice
Group therapy provides a safe space for role-playing difficult scenarios such as refusing drugs at a party or handling stress without substances. Practicing these situations in a group builds confidence and prepares individuals for real-life encounters.
4. Peer Accountability and Support
Support from peers is one of the most powerful aspects of group therapy. Knowing that others understand your journey and are watching out for you can be a motivating factor. Group members often form bonds that extend outside therapy, offering continuous reinforcement of positive behavior.
5. Journaling and Self-Reflection
Participants are encouraged to maintain journals to track their feelings, thoughts, and behavioral patterns. Reviewing these in a group setting helps identify triggers and reinforces the use of healthy coping mechanisms.
6. Developing Healthy Routines
Group sessions stress the importance of structure. From setting wake-up times to scheduling exercise, participants learn how routine can reduce anxiety and minimize opportunities for relapse.
7. Learning Communication Skills
Many individuals in recovery struggle with expressing emotions. Group therapy teaches assertive communication, conflict resolution, and how to ask for help — all vital for maintaining healthy relationships and boundaries.
8. Emotional Regulation Techniques
These include techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and grounding exercises. Participants are trained to use these during high-stress situations, thereby reducing the risk of relapse.
9. Setting and Achieving Small Goals
Group members are encouraged to set achievable short-term goals. Whether it’s attending a meeting, applying for a job, or reconnecting with family, small wins build momentum and self-confidence.
10. Building a Sober Social Network
Isolation is a major trigger for relapse. Through group therapy, individuals form social networks that support sobriety and reduce the sense of loneliness that often accompanies addiction recovery.
How Group Therapy Facilitates Strategy Implementation
Group therapy is more than just conversation. It is a dynamic environment where participants:
- Practice and refine strategies in real-time.
- Get constructive feedback.
- See the impact of strategies through others’ success.
- Develop empathy and learn vicariously.
Therapists guide the process by assigning homework, facilitating role-playing, and monitoring group dynamics to ensure each person grows in their coping skills.
Real-Life Impact of Coping Strategies in Group Therapy
Let’s consider a case example:
John, a recovering opioid user, struggled with relapse after periods of stress. Through group therapy, he learned to identify early warning signs, journal his emotional states, and call a peer instead of using. With weekly support and accountability, John achieved six months of sobriety — his longest period in years.
Such transformations are not rare. When effective coping strategies in substance abuse group therapy are practiced consistently, they lay a strong foundation for lifelong recovery.
Table: Summary of Strategies and Their Benefits
| Coping Strategy | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Restructuring | Replaces negative thinking with constructive views |
| Mindfulness & Meditation | Enhances focus and emotional stability |
| Role-Playing | Prepares individuals for real-life challenges |
| Peer Support | Builds connection and reduces isolation |
| Journaling | Promotes self-awareness and growth |
| Healthy Routines | Reduces idle time and enhances stability |
| Communication Skills | Improves relationships and support-seeking |
| Emotional Regulation | Prevents emotional relapse |
| Goal Setting | Boosts motivation and tracks progress |
| Sober Social Network | Offers continuous, non-judgmental support |
Conclusion
Effective coping strategies in substance abuse group therapy are essential pillars of long-term recovery. From mindfulness and cognitive restructuring to goal-setting and emotional regulation, these tools equip individuals to manage real-life challenges without turning to substances. Group therapy enhances these strategies by providing structure, support, and a sense of belonging — key elements for a sustainable, sober life.
FAQs About Coping Strategies in Substance Abuse Group Therapy
- Can coping strategies from group therapy be used outside of sessions?
Yes, these strategies are designed to be practiced in daily life to support long-term recovery. - What happens if someone struggles to implement a coping strategy?
Therapists and peers provide feedback and adjustments to ensure the strategy fits the individual’s needs. - Are coping strategies the same for everyone?
No, strategies are personalized based on the individual’s triggers, goals, and personality. - Is it possible to relapse even with coping strategies in place?
Yes, relapse can occur. However, coping strategies help reduce frequency and severity and aid in faster recovery. - How long does it take to see results from using these strategies?
Results vary, but consistent use typically leads to noticeable improvement within weeks. - Do group therapy sessions change over time?
Yes, sessions evolve as participants grow, focusing on deeper issues and advanced strategies. - Can family members learn about these coping strategies?
Some programs include family education sessions to help them support the recovery process. - Is it necessary to have a therapist to use these strategies?
While guidance is beneficial, many strategies can be self-applied once learned. - Are these strategies useful for co-occurring disorders?
Yes, many coping tools overlap with those used in treating anxiety, depression, and trauma. - What is the difference between coping and avoidance?
Coping addresses problems directly, while avoidance delays dealing with them — which can worsen the situation.